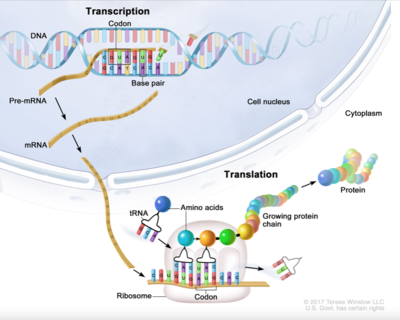
Transcription
Transcription is the process by which a cell makes an RNA copy of a piece of DNA. This RNA copy called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the genetic information needed to make proteins in a cell. It carries the information from the DNA in the cell's nucleus to the cytoplasm, where proteins are made.
The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples.
Less than 2% of the human genome can be transcribed into mRNA, while at least 80% of mammalian genomic DNA can be actively transcribed (in one or more types of cells), with the majority of this 80% considered to be ncRNA.